 |
| What Causes Rosacea |What Helps Rosacea | How To Get Rid Of Rosacea Permanently |
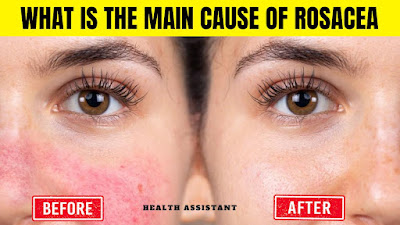
It is not entirely clear what causes rosacea, but some factors that may play a role include genetics, abnormal blood vessels in the face, and a reaction to certain microscopic mites or bacteria on the skin. Certain lifestyle factors such as sun exposure, alcohol consumption, and spicy foods may exacerbate symptoms.
Treatment may include creams, gels, and oral medications to reduce inflammation, minimize redness, and control symptoms.
It is important to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
What Causes Rosacea - What Is The Main Cause of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea is not known, but a number of factors may contribute to its development, including:
Genetics: Studies suggest that people with a family history of rosacea may be more likely to develop the condition.
Abnormal blood vessels: Rosacea may be related to the dilation of blood vessels in the face, which causes redness and flushing.
Microscopic mites: Demodex mites, which are commonly found on the skin, may play a role in the development of rosacea.
Bacteria: Certain bacteria, such as the H. pylori bacteria that can cause stomach ulcers, have been found in higher levels in people with rosacea.
Immune system: Some researchers believe that an overactive immune system may contribute to the development of rosacea.
Environmental factors: Sun exposure, wind, cold, heat, and certain skin care products may cause flare-ups of rosacea.
Lifestyle factors: Alcohol consumption, spicy foods, and emotional stress may also exacerbate rosacea symptoms.
It is important to note that the causes of rosacea are not fully understood and more research is needed to determine the exact underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of the condition.
What Helps Rosacea
Treatment for rosacea can help reduce inflammation, minimize redness, and control symptoms. The treatment plan may vary depending on the severity and presentation of the rosacea, as well as the individual's preference.
Topical therapy: Creams, gels, and lotions containing metronidazole, azelaic acid, or sulfur can help reduce inflammation and redness.
Oral medications: Antibiotics such as tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline can help reduce inflammation and the overgrowth of certain bacteria that may contribute to rosacea.
Isotretinoin: This oral medication is used for severe or persistent cases of rosacea that do not respond to other treatments.
Light-based therapy: Intense Pulse Light (IPL) and laser therapy can help reduce redness and visible blood vessels.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be used to remove excess tissue or correct disfigurement caused by rosacea.
Lifestyle changes: Sun protection, avoiding triggers, such as spicy foods and alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy skincare routine can help control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
It is essential to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan and to be re-evaluated regularly. Self-treatment or using the over-the-counter medication without a proper diagnosis can worsen the condition or cause other side effects.
How To Get Rid Of Rosacea Permanently
There is currently no known cure for rosacea, however, the condition can be managed effectively with appropriate treatment.
While there is no permanent cure for rosacea, treatment can help control symptoms and prevent flare-ups. This typically includes a combination of topical and oral medications, as well as lifestyle changes.
Some of the treatment options that can help improve the symptoms of rosacea include:
Topical therapy: Creams, gels, and lotions containing metronidazole, azelaic acid, or sulfur can help reduce inflammation and redness.
Oral medications: Antibiotics such as tetracycline, doxycycline, or minocycline can help reduce inflammation and the overgrowth of certain bacteria that may contribute to rosacea.
Isotretinoin: This oral medication is used for severe or persistent cases of rosacea that do not respond to other treatments.
Light-based therapy: Intense Pulse Light (IPL) and laser therapy can help reduce redness and visible blood vessels.
Surgery: In rare cases, surgery may be used to remove excess tissue or correct disfigurement caused by rosacea.
Lifestyle changes: Sun protection, avoiding triggers such as spicy foods and alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy skincare routine can help control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop an appropriate treatment plan, and to be re-evaluated regularly. Keep in mind that rosacea is a chronic condition that requires long-term management, and symptoms may recur even with treatment.
Your face looks like you are blushing and you get bumps that are a bit like acne, you might have a skin condition called rosacea. Your doctor can suggest medicine and other treatments to manage your symptoms, and there are plenty of steps you can take at home to make yourself look and feel better.
What causes rosacea?
The cause of rosacea has not been determined. It may be a combination of hereditary and environmental factors. It is known that some things may make your rosacea symptoms worse. These include:
- eating spicy foods
- eating items that contain the compound cinnamaldehyde, such as cinnamon, chocolate, tomatoes, and citrus
- drinking hot coffee or tea
- having the intestinal bacteria Helicobacter pylori
- a skin mite called Demodex and the bacterium it carries, Bacillus Polonius
- the presence of cathelicidin (a protein that protects the skin from infection)
Types of rosacea
The four types of rosacea are:
1. Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR), is associated with facial redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels.
2. Papulopustular (or acne) rosacea, is associated with acne-like breakouts and often affects middle-aged women.
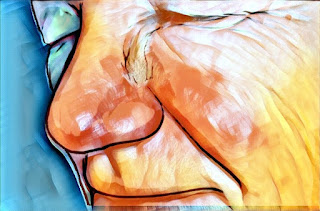
3. Rhinophyma, is a rare form associated with the thickening of the skin on your nose. It usually affects men and is often accompanied by another subtype of rosacea.
4. Ocular rosacea and its symptoms are centered on the eye area.







0 Comments